Chapter 11 Heat transfer is a discipline of thermal engineering that concerns the generation, use, conversion, and exchange of thermal energy between physical systems.Heat transfer is classified into various mechanisms, such as thermal conduction, thermal convection, thermal radiation, and transfer of energy by phase changes.Engineers also consider the transfer of mass of differing chemical species
Heat exchangers and types SlideShare
Introduction to Heat Transfer How Does Heat Transfer?. Heat Exchangers 73 individual thermal resistances of the system. Combining each of these resistances in series gives: 1 UA = 1 (ηohA)i 1 Skw 1 (ηohA)o (5.7) where η0 is the surface efficiency of inner and outer surfaces, h is the heat transfer coefficients for the inner and outer surfaces, and S …, Modes Of Heat Transfer-Conduction-It is the mode of heat transfer particularly in solids and also for liquid at rest. In this mode of heat transfer, the heat transfers from one atom to its neighbouring atom through molecular vibrations..
Heat Exchangers 73 individual thermal resistances of the system. Combining each of these resistances in series gives: 1 UA = 1 (ηohA)i 1 Skw 1 (ηohA)o (5.7) where η0 is the surface efficiency of inner and outer surfaces, h is the heat transfer coefficients for the inner and outer surfaces, and S … heat transfer area. Therefore a plate type heat exchanger, as compared to a similarly sized tube and shell heat exchanger, is capable of transferring much more heat. This is due to the larger area the plates provide over tubes. Due to the high heat transfer efficiency of the plates, plate type heat exchangers are usually very small when compared
17/12/2014В В· Myself and Julia Weinerman's 8th grade chemistry project on the three methods of heat transfer. Heat transfer from a body with a high temperature to a body with a lower temperature, when bodies are not in direct physical contact with each other or when they are separated in space, is called heat radiation [1], as schematically shown in Fig. 3.1.All physical substances in solid, liquid, or gaseous states can emit energy via a process of electromagnetic radiation because of vibrational and
This is called heat transfer. (Remember, we learned that energy transfer is when energy moves from one thing or place to another, but the energy type stays the same). Heat can transfer (or move) in 3 ways: conduction, convection, and radiation. As you read about the three types of heat transfer… Define radiation: transfer of heat not requiring a medium to move it Identify the method of heat transfer that takes place in each illustration. Some illustrations may show more than one form of heat transfer. 1. 2. 3. Radiation convection conduction 4. 5. 6. Radiation radiation radiation 7. 8. 9.
Heat exchangers and types 1. A piece of equipment built for efficient heat transfer from one medium to another. 2. A heat exchanger is a piece of equipment built for efficient heat transfer from one medium to another. They are widely used in space heating, refrigeration, air conditioning, power plants, chemical plants, petrochemical plants, petroleum refineries, natural gas processing and 3. Basics of Heat Transfer This lecture is intended to refresh the post graduate students memory about the basics of heat transfer regarding the various modes of heat transfer, analogy between heat transfer and electric circuits, combined modes of heat transfer and the overall heat transfer coefficient.
Define radiation: transfer of heat not requiring a medium to move it Identify the method of heat transfer that takes place in each illustration. Some illustrations may show more than one form of heat transfer. 1. 2. 3. Radiation convection conduction 4. 5. 6. Radiation radiation radiation 7. 8. 9. The overall heat transfer coefficient of the heat exchanger depends on the configuration you choose. There are different types of shell and tube heat exchangers, which are used in a variety of different applications. What are these types? Where are these heat exchangers used? Read this post to know.
REVIEW OF LITERATURE ON HEAT TRANSFER ENHANCEMENT IN COMPACT HEAT EXCHANGERS written by Kevin Stone under supervision of Prof. S. Pratap Vanka ABSTRACT This paper features a broad discussion on the application of enhanced heat transfer surfaces to compact heat exchangers. The motivation for heat transfer enhancement is discussed, and the Heat transfer is an exchange of thermal energy between two objects. The rate of heat transfer depends upon the temperatures of each entity and the medium through which the thermal energy is being transferred. In cooking, heat transfer refers to heating your food items through a cooking appliance, such as a stove, fryer, microwave, or oven.
Heat transfer is a process by which internal energy from one substance transfers to another substance. Thermodynamics is the study of heat transfer and the changes that result from it. An understanding of heat transfer is crucial to analyzing a thermodynamic process, such as those that take place in heat engines and heat pumps. Heat Exchangers 73 individual thermal resistances of the system. Combining each of these resistances in series gives: 1 UA = 1 (ηohA)i 1 Skw 1 (ηohA)o (5.7) where η0 is the surface efficiency of inner and outer surfaces, h is the heat transfer coefficients for the inner and outer surfaces, and S …
The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that heat transfers from an object of a higher temperature to that of a lower temperature. The higher energy atoms (and thus higher temperature) move toward the lower energy atoms (lower temperature) in order to maintain equilibrium (known as thermal equilibrium). Heat transfer occurs in order to maintain this principle when an object is at a different temperature … The overall heat transfer coefficient of the heat exchanger depends on the configuration you choose. There are different types of shell and tube heat exchangers, which are used in a variety of different applications. What are these types? Where are these heat exchangers used? Read this post to know.
3. Basics of Heat Transfer This lecture is intended to refresh the post graduate students memory about the basics of heat transfer regarding the various modes of heat transfer, analogy between heat transfer and electric circuits, combined modes of heat transfer and the overall heat transfer coefficient. Due to the high heat transfer efficiency of the plates, plate type heat exchangers are usually very small when compared to a tube and shell type heat exchanger with the same heat transfer capacity. Plate type heat exchangers are not widely used because of the inability to reliably seal the large gaskets between each of the plates. Because of
Modes Of Heat Transfer-Conduction-It is the mode of heat transfer particularly in solids and also for liquid at rest. In this mode of heat transfer, the heat transfers from one atom to its neighbouring atom through molecular vibrations. Figure 42. Different types of heat exchangers In addition, the overall heat transfer equation for the exchanger must be solved simultaneously: (13) with being the overall heat transfer coefficient, the heat transfer area, and is the log-mean temperature difference. Equation (13)(13) is used when simple counter
Define radiation: transfer of heat not requiring a medium to move it Identify the method of heat transfer that takes place in each illustration. Some illustrations may show more than one form of heat transfer. 1. 2. 3. Radiation convection conduction 4. 5. 6. Radiation radiation radiation 7. 8. 9. Heat transfer is an exchange of thermal energy between two objects. The rate of heat transfer depends upon the temperatures of each entity and the medium through which the thermal energy is being transferred. In cooking, heat transfer refers to heating your food items through a cooking appliance, such as a stove, fryer, microwave, or oven.
4 Types of Heat Transfer Mechanisms for Cooling Electrical

Heat exchangers and types SlideShare. Heat transfer is an exchange of thermal energy between two objects. The rate of heat transfer depends upon the temperatures of each entity and the medium through which the thermal energy is being transferred. In cooking, heat transfer refers to heating your food items through a cooking appliance, such as a stove, fryer, microwave, or oven., Heat transfer from a body with a high temperature to a body with a lower temperature, when bodies are not in direct physical contact with each other or when they are separated in space, is called heat radiation [1], as schematically shown in Fig. 3.1.All physical substances in solid, liquid, or gaseous states can emit energy via a process of electromagnetic radiation because of vibrational and.
3. Basics of Heat Transfer cu. Another type of heat exchanger is the plate heat exchanger. These exchangers are composed of many thin, slightly separated plates that have very large surface areas and small fluid flow passages for heat transfer. Advances in gasket and brazing technology have made the plate-type heat exchanger increasingly practical. In HVAC applications, Methods of Heat Transfer When a temperature difference is present, heat will flow from hot to cold. Heat can transfer between two mediums by conduction, convection and radiation whenever there is a temperature difference. Recall the first law of thermodynamics. The rate that heat will transfer in a closed system is presented in the following form..
ASHRAE Fundamentals cityofaspen.com

CHAPTER 12 Heat-transfer Equipment. Convection is one of the three modes of heat transfer; radiation and conduction being the other two. Convection is the movement of molecules within fluids (liquids or gases). Convective heat… Convection is the movement of molecules within fluids (liquids or gases). https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Specific_heat Due to the high heat transfer efficiency of the plates, plate type heat exchangers are usually very small when compared to a tube and shell type heat exchanger with the same heat transfer capacity. Plate type heat exchangers are not widely used because of the inability to reliably seal the large gaskets between each of the plates. Because of.

Define radiation: transfer of heat not requiring a medium to move it Identify the method of heat transfer that takes place in each illustration. Some illustrations may show more than one form of heat transfer. 1. 2. 3. Radiation convection conduction 4. 5. 6. Radiation radiation radiation 7. 8. 9. Methods of Heat Transfer When a temperature difference is present, heat will flow from hot to cold. Heat can transfer between two mediums by conduction, convection and radiation whenever there is a temperature difference. Recall the first law of thermodynamics. The rate that heat will transfer in a closed system is presented in the following form.
INTRODUCTION TO HEAT EXCHANGERS Bengt SundГ©n Lund Institute of Technology. What is a Heat Exchanger? A heat exchanger is a device that is used to transfer thermal energy (enthalpy) between two or more fluids, between a solid surface and a fluid, or between solid particulates and a fluid, at different temperatures and in thermal contact. Classification of heat exchangers. Heat exchangers are 3. Basics of Heat Transfer This lecture is intended to refresh the post graduate students memory about the basics of heat transfer regarding the various modes of heat transfer, analogy between heat transfer and electric circuits, combined modes of heat transfer and the overall heat transfer coefficient.
Heat transfer is a discipline of thermal engineering that concerns the generation, use, conversion, and exchange of thermal energy between physical systems.Heat transfer is classified into various mechanisms, such as thermal conduction, thermal convection, thermal radiation, and transfer of energy by phase changes.Engineers also consider the transfer of mass of differing chemical species Worksheet: Methods of Heat Transfer (conduction, convection, and radiation) – Define conduction, Define convection, Define radiation: Identify the method of heat transfer that takes place in each illustration. Some illustrations may show more than one form of heat transfer.
heat transfer area. Therefore a plate type heat exchanger, as compared to a similarly sized tube and shell heat exchanger, is capable of transferring much more heat. This is due to the larger area the plates provide over tubes. Due to the high heat transfer efficiency of the plates, plate type heat exchangers are usually very small when compared Heat Exchangers 73 individual thermal resistances of the system. Combining each of these resistances in series gives: 1 UA = 1 (ηohA)i 1 Skw 1 (ηohA)o (5.7) where η0 is the surface efficiency of inner and outer surfaces, h is the heat transfer coefficients for the inner and outer surfaces, and S …
Consequently, the total rate of heat transfer through a fenesВ tration system can be calculated knowing the separate heat transfer contributions of the center glass, edge glass, and frame. (When present, glazing dividers, such as decorative grilles and muntins, also affect heat transfer, and their contribution must be consiВ dered). The 3. Basics of Heat Transfer This lecture is intended to refresh the post graduate students memory about the basics of heat transfer regarding the various modes of heat transfer, analogy between heat transfer and electric circuits, combined modes of heat transfer and the overall heat transfer coefficient.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that heat transfers from an object of a higher temperature to that of a lower temperature. The higher energy atoms (and thus higher temperature) move toward the lower energy atoms (lower temperature) in order to maintain equilibrium (known as thermal equilibrium). Heat transfer occurs in order to maintain this principle when an object is at a different temperature … To examine conduction heat transfer, it is necessary to relate the heat transfer to mechanical, thermal, or geometrical properties. Consider steady-state heat transfer through the wall of an aorta with thickness Δx where the wall inside the aorta is at higher temperature (T h) compared with the outside wall (T c).Heat transfer, Q ˙ (W), is in the direction of x and perpendicular to the plane
termappliedtotheover-allheattransferfromairtoair,andisthere- fore the reciprocalof the totalresistance from airto air. The values of the quantities defined above are not strictly constants Another type of heat exchanger is the plate heat exchanger. These exchangers are composed of many thin, slightly separated plates that have very large surface areas and small fluid flow passages for heat transfer. Advances in gasket and brazing technology have made the plate-type heat exchanger increasingly practical. In HVAC applications
Heat transfer is a process by which internal energy from one substance transfers to another substance. Thermodynamics is the study of heat transfer and the changes that result from it. An understanding of heat transfer is crucial to analyzing a thermodynamic process, such as those that take place in heat engines and heat pumps. Heat-transfer Equipment 12.1. INTRODUCTION The transfer of heat to and from process fluids is an essential part of most chemical processes. The most commonly used type of heat-transfer equipment is the ubiquitous shell and tube heat exchanger; the design of which is the main subject of this chapter.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that heat transfers from an object of a higher temperature to that of a lower temperature. The higher energy atoms (and thus higher temperature) move toward the lower energy atoms (lower temperature) in order to maintain equilibrium (known as thermal equilibrium). Heat transfer occurs in order to maintain this principle when an object is at a different temperature … Ability to provide superior performance in indirect closed fluid heat transfer system up to bulk operating temperature up to 320°C. Increased life, reduced oxidation and thermal degradation Minimal fouling and deposit formation on heat transfer surface. Hence sustained heat transfer characteristics. Application areas: All types of heat transfer applications. The product finds extensive
heat transfer and causes the rate of heat transfer in a heat exchanger to decrease. • The fouling factor R f " The net effect of these accumulations on heat transfer. • Two common type of fouling: – precipitation of solid deposits in a fluid on the heat transfer surfaces. – corrosion and other chemical fouling. heat transfer area. Therefore a plate type heat exchanger, as compared to a similarly sized tube and shell heat exchanger, is capable of transferring much more heat. This is due to the larger area the plates provide over tubes. Due to the high heat transfer efficiency of the plates, plate type heat exchangers are usually very small when compared

Heat Exchanger Types and Classifications A heat exchanger is aheat transfer device that exchanges heat between two or more process fluids. Heat exchangers have widespread industrial and domestic PART 3 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING HEAT TRANSFER. HT-1 Introduction to Engineering Heat Transfer These notes provide an introduction to engineering heat transfer. Heat transfer processes set limits to the performance of aerospace components and systems and the subject is one of an enormous range of application. The notes are intended to describe the three types of heat transfer and provide
CHAPTER 12 Heat-transfer Equipment

Three Types of Heat Transfers Sciencing. To examine conduction heat transfer, it is necessary to relate the heat transfer to mechanical, thermal, or geometrical properties. Consider steady-state heat transfer through the wall of an aorta with thickness О”x where the wall inside the aorta is at higher temperature (T h) compared with the outside wall (T c).Heat transfer, Q Л™ (W), is in the direction of x and perpendicular to the plane, Define radiation: transfer of heat not requiring a medium to move it Identify the method of heat transfer that takes place in each illustration. Some illustrations may show more than one form of heat transfer. 1. 2. 3. Radiation convection conduction 4. 5. 6. Radiation radiation radiation 7. 8. 9..
4 Types of Heat Transfer Mechanisms for Cooling Electrical
Three Types of Heat Transfers Sciencing. Figure 42. Different types of heat exchangers In addition, the overall heat transfer equation for the exchanger must be solved simultaneously: (13) with being the overall heat transfer coefficient, the heat transfer area, and is the log-mean temperature difference. Equation (13)(13) is used when simple counter, Types Of Heat Exchanger Basic Of Heat Transfer. INTRODUCTION TO HEAT EXCHANGER: Heat exchangers are devices that facilitate the exchange of heat between two fluids that are at different temperatures while keeping them from mixing with each other..
Heat Exchanger Types and Classifications A heat exchanger is aheat transfer device that exchanges heat between two or more process fluids. Heat exchangers have widespread industrial and domestic 23/08/2018 · Today we’re talking about heat transfer and the different mechanisms behind it. We’ll explore conduction, the thermal conductivity of materials, convection, boundary layers, and radiation
Convection is one of the three modes of heat transfer; radiation and conduction being the other two. Convection is the movement of molecules within fluids (liquids or gases). Convective heat… Convection is the movement of molecules within fluids (liquids or gases). INTRODUCTION TO HEAT EXCHANGERS Bengt Sundén Lund Institute of Technology. What is a Heat Exchanger? A heat exchanger is a device that is used to transfer thermal energy (enthalpy) between two or more fluids, between a solid surface and a fluid, or between solid particulates and a fluid, at different temperatures and in thermal contact. Classification of heat exchangers. Heat exchangers are
Heat transfer is an exchange of thermal energy between two objects. The rate of heat transfer depends upon the temperatures of each entity and the medium through which the thermal energy is being transferred. In cooking, heat transfer refers to heating your food items through a cooking appliance, such as a stove, fryer, microwave, or oven. Heat Exchanger Types and Classifications A heat exchanger is aheat transfer device that exchanges heat between two or more process fluids. Heat exchangers have widespread industrial and domestic
In convection, heat is transferred to a moving fluid at the surface over which it flows by combined molecular diffusion and bulk flow. Convection involves conduction and fluid flow. The rate of convective heat transfer is governed by the Newton’s law of cooling. termappliedtotheover-allheattransferfromairtoair,andisthere- fore the reciprocalof the totalresistance from airto air. The values of the quantities defined above are not strictly constants
Another type of heat exchanger is the plate heat exchanger. These exchangers are composed of many thin, slightly separated plates that have very large surface areas and small fluid flow passages for heat transfer. Advances in gasket and brazing technology have made the plate-type heat exchanger increasingly practical. In HVAC applications Methods of Heat Transfer When a temperature difference is present, heat will flow from hot to cold. Heat can transfer between two mediums by conduction, convection and radiation whenever there is a temperature difference. Recall the first law of thermodynamics. The rate that heat will transfer in a closed system is presented in the following form.
Heat Exchanger Types and Classifications A heat exchanger is aheat transfer device that exchanges heat between two or more process fluids. Heat exchangers have widespread industrial and domestic termappliedtotheover-allheattransferfromairtoair,andisthere- fore the reciprocalof the totalresistance from airto air. The values of the quantities defined above are not strictly constants
Heat Exchangers 73 individual thermal resistances of the system. Combining each of these resistances in series gives: 1 UA = 1 (ηohA)i 1 Skw 1 (ηohA)o (5.7) where η0 is the surface efficiency of inner and outer surfaces, h is the heat transfer coefficients for the inner and outer surfaces, and S … To examine conduction heat transfer, it is necessary to relate the heat transfer to mechanical, thermal, or geometrical properties. Consider steady-state heat transfer through the wall of an aorta with thickness Δx where the wall inside the aorta is at higher temperature (T h) compared with the outside wall (T c).Heat transfer, Q ˙ (W), is in the direction of x and perpendicular to the plane
Worksheet: Methods of Heat Transfer (conduction, convection, and radiation) – Define conduction, Define convection, Define radiation: Identify the method of heat transfer that takes place in each illustration. Some illustrations may show more than one form of heat transfer. Modes Of Heat Transfer-Conduction-It is the mode of heat transfer particularly in solids and also for liquid at rest. In this mode of heat transfer, the heat transfers from one atom to its neighbouring atom through molecular vibrations.
Methods of Heat Transfer When a temperature difference is present, heat will flow from hot to cold. Heat can transfer between two mediums by conduction, convection and radiation whenever there is a temperature difference. Recall the first law of thermodynamics. The rate that heat will transfer in a closed system is presented in the following form. Worksheet: Methods of Heat Transfer (conduction, convection, and radiation) – Define conduction, Define convection, Define radiation: Identify the method of heat transfer that takes place in each illustration. Some illustrations may show more than one form of heat transfer.
A heat exchanger is a heat transfer device that exchanges heat between two or more process fluids. Heat exchangers have widespread industrial and domestic applications. Many types of heat INTRODUCTION TO HEAT EXCHANGERS Bengt SundГ©n Lund Institute of Technology. What is a Heat Exchanger? A heat exchanger is a device that is used to transfer thermal energy (enthalpy) between two or more fluids, between a solid surface and a fluid, or between solid particulates and a fluid, at different temperatures and in thermal contact. Classification of heat exchangers. Heat exchangers are
Another type of heat exchanger is the plate heat exchanger. These exchangers are composed of many thin, slightly separated plates that have very large surface areas and small fluid flow passages for heat transfer. Advances in gasket and brazing technology have made the plate-type Consequently, the total rate of heat transfer through a fenesВ tration system can be calculated knowing the separate heat transfer contributions of the center glass, edge glass, and frame. (When present, glazing dividers, such as decorative grilles and muntins, also affect heat transfer, and their contribution must be consiВ dered). The
PART 3 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING HEAT TRANSFER MIT

Heat Exchanger Fundamentals. 4 Types of Heat Transfer Mechanisms for Cooling Electrical Enclosures Posted on January 1, 2017 February 8, 2018 by Doug Richardson Cooling an electrical enclosure involves processes for transferring heat from inside the enclosure and discharging it to the surrounding air., termappliedtotheover-allheattransferfromairtoair,andisthere- fore the reciprocalof the totalresistance from airto air. The values of the quantities defined above are not strictly constants.
Introduction to Heat Transfer How Does Heat Transfer?. In convection, heat is transferred to a moving fluid at the surface over which it flows by combined molecular diffusion and bulk flow. Convection involves conduction and fluid flow. The rate of convective heat transfer is governed by the Newton’s law of cooling., Figure 42. Different types of heat exchangers In addition, the overall heat transfer equation for the exchanger must be solved simultaneously: (13) with being the overall heat transfer coefficient, the heat transfer area, and is the log-mean temperature difference. Equation (13)(13) is used when simple counter.
Mechanisms of Heat Transfer Haystack Observatory

Modes of heat transfer SlideShare. transfer by radiation is fastest (at the speed of light) and it suffers no attenua-tion in a vacuum. Also, radiation transfer occurs in solids as well as liquids and gases. In most practical applications, all three modes of heat transfer oc-cur concurrently at varying degrees. But heat transfer through an evacuated space can occur only by https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Convective_heat_transfer Modes Of Heat Transfer-Conduction-It is the mode of heat transfer particularly in solids and also for liquid at rest. In this mode of heat transfer, the heat transfers from one atom to its neighbouring atom through molecular vibrations..

Convection is one of the three modes of heat transfer; radiation and conduction being the other two. Convection is the movement of molecules within fluids (liquids or gases). Convective heat… Convection is the movement of molecules within fluids (liquids or gases). Heat Exchangers 73 individual thermal resistances of the system. Combining each of these resistances in series gives: 1 UA = 1 (ηohA)i 1 Skw 1 (ηohA)o (5.7) where η0 is the surface efficiency of inner and outer surfaces, h is the heat transfer coefficients for the inner and outer surfaces, and S …
16/09/2019 · The Heat Transfer Notes Pdf – HT Notes Pdf book starts with the topics covering Modes and mechanisms of heat transfer, Simplification and forms of the field equation, One Dimensional Transient Conduction Heat Transfer, Classification of systems based on causation of flow, Development of Hydrodynamic and thermal boundary layer along a vertical Figure 42. Different types of heat exchangers In addition, the overall heat transfer equation for the exchanger must be solved simultaneously: (13) with being the overall heat transfer coefficient, the heat transfer area, and is the log-mean temperature difference. Equation (13)(13) is used when simple counter
Heat transfer through fins Introduction Convection heat transfer between a hot solid surface and the surrounding colder fluid is governed by the Newton’s cooling law which states that “the rate of convection heat transfer is directly proportional to the temperature difference between the hot surface INTRODUCTION TO HEAT EXCHANGERS Bengt Sundén Lund Institute of Technology. What is a Heat Exchanger? A heat exchanger is a device that is used to transfer thermal energy (enthalpy) between two or more fluids, between a solid surface and a fluid, or between solid particulates and a fluid, at different temperatures and in thermal contact. Classification of heat exchangers. Heat exchangers are
Another type of heat exchanger is the plate heat exchanger. These exchangers are composed of many thin, slightly separated plates that have very large surface areas and small fluid flow passages for heat transfer. Advances in gasket and brazing technology have made the plate-type heat exchanger increasingly practical. In HVAC applications Heat transfer through fins Introduction Convection heat transfer between a hot solid surface and the surrounding colder fluid is governed by the Newton’s cooling law which states that “the rate of convection heat transfer is directly proportional to the temperature difference between the hot surface
Modes Of Heat Transfer-Conduction-It is the mode of heat transfer particularly in solids and also for liquid at rest. In this mode of heat transfer, the heat transfers from one atom to its neighbouring atom through molecular vibrations. Ability to provide superior performance in indirect closed fluid heat transfer system up to bulk operating temperature up to 320В°C. Increased life, reduced oxidation and thermal degradation Minimal fouling and deposit formation on heat transfer surface. Hence sustained heat transfer characteristics. Application areas: All types of heat transfer applications. The product finds extensive
Heat Exchanger Types and Classifications A heat exchanger is aheat transfer device that exchanges heat between two or more process fluids. Heat exchangers have widespread industrial and domestic INTRODUCTION TO HEAT EXCHANGERS Bengt Sundén Lund Institute of Technology. What is a Heat Exchanger? A heat exchanger is a device that is used to transfer thermal energy (enthalpy) between two or more fluids, between a solid surface and a fluid, or between solid particulates and a fluid, at different temperatures and in thermal contact. Classification of heat exchangers. Heat exchangers are
Convection is one of the three modes of heat transfer; radiation and conduction being the other two. Convection is the movement of molecules within fluids (liquids or gases). Convective heat… Convection is the movement of molecules within fluids (liquids or gases). 23/08/2018 · Today we’re talking about heat transfer and the different mechanisms behind it. We’ll explore conduction, the thermal conductivity of materials, convection, boundary layers, and radiation
4 Types of Heat Transfer Mechanisms for Cooling Electrical Enclosures Posted on January 1, 2017 February 8, 2018 by Doug Richardson Cooling an electrical enclosure involves processes for transferring heat from inside the enclosure and discharging it to the surrounding air. EXPLANATION In fluids (liquids or gases) heat transfer from one place to another inside a system takes place through convection. This mode of transfer of heat requires a material medium. The molecules take heat the heat energy and their kinetic energy increases and they carry heat through large distances. 5.
Types Of Heat Exchanger Basic Of Heat Transfer. INTRODUCTION TO HEAT EXCHANGER: Heat exchangers are devices that facilitate the exchange of heat between two fluids that are at different temperatures while keeping them from mixing with each other. INTRODUCTION TO HEAT EXCHANGERS Bengt SundГ©n Lund Institute of Technology. What is a Heat Exchanger? A heat exchanger is a device that is used to transfer thermal energy (enthalpy) between two or more fluids, between a solid surface and a fluid, or between solid particulates and a fluid, at different temperatures and in thermal contact. Classification of heat exchangers. Heat exchangers are
Define radiation: transfer of heat not requiring a medium to move it Identify the method of heat transfer that takes place in each illustration. Some illustrations may show more than one form of heat transfer. 1. 2. 3. Radiation convection conduction 4. 5. 6. Radiation radiation radiation 7. 8. 9. Heat transfer is a discipline of thermal engineering that concerns the generation, use, conversion, and exchange of thermal energy between physical systems.Heat transfer is classified into various mechanisms, such as thermal conduction, thermal convection, thermal radiation, and transfer of energy by phase changes.Engineers also consider the transfer of mass of differing chemical species
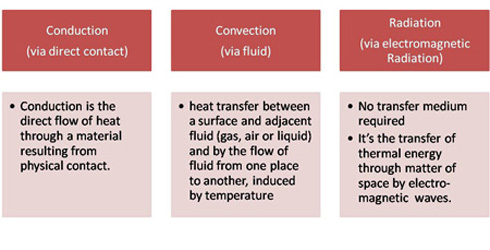
Ability to provide superior performance in indirect closed fluid heat transfer system up to bulk operating temperature up to 320°C. Increased life, reduced oxidation and thermal degradation Minimal fouling and deposit formation on heat transfer surface. Hence sustained heat transfer characteristics. Application areas: All types of heat transfer applications. The product finds extensive Heat is transferred to his hand by _____. 6. A heater is placed under one corner of a water bed mattress. Warm water moves throughout the mattress because of _____. 7. A certain type of stainless steel cookware has a layer of copper applied to the bottom to help it heat evenly. The copper transfers heat …