bipap settings pdf
BiPAP settings are crucial for effective therapy, tailored to individual patient needs․ Proper configuration ensures comfort and efficacy, addressing sleep apnea and respiratory conditions․ Clinical guidelines and patient-specific adjustments guide optimal setup, ensuring therapeutic benefits and minimizing discomfort․ Understanding these settings is key to successful BiPAP therapy․
Overview of BiPAP Therapy
BiPAP therapy, or bi-level positive airway pressure, is a non-invasive ventilation method that delivers two levels of air pressure: higher during inhalation (IPAP) and lower during exhalation (EPAP)․ This dual-pressure system supports patients with respiratory conditions like sleep apnea, COPD, or acute respiratory failure․ The therapy is tailored to individual needs, ensuring comfortable breathing and preventing airway collapse․ BiPAP devices are equipped with features like heated humidifiers and adjustable settings to enhance comfort and efficacy․ Proper titration of IPAP and EPAP levels is essential for optimal therapy outcomes․ Healthcare providers often refer to guidelines and patient-specific data to configure these settings effectively, ensuring both therapeutic benefits and patient comfort․
Importance of Proper BiPAP Settings
Proper BiPAP settings are vital for effective treatment of respiratory conditions․ Incorrect settings can lead to inadequate therapy, discomfort, or complications․ Optimally configured IPAP and EPAP levels ensure airway patency, improve sleep quality, and prevent respiratory events․ Proper settings also reduce the risk of side effects like mask leaks or pressure intolerance․ Clinicians rely on patient-specific data, such as tidal volumes and respiratory rates, to fine-tune settings․ Regular monitoring and adjustments are essential to maintain therapeutic efficacy and patient comfort․ Adhering to clinical guidelines and manufacturer recommendations ensures safe and effective BiPAP therapy, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes and quality of life․
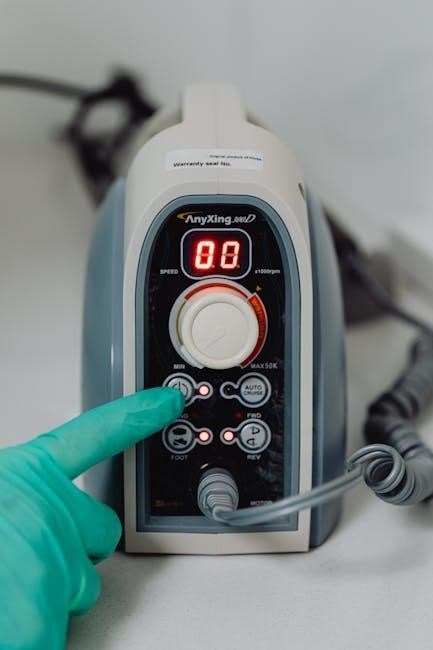
Understanding BiPAP Machine Components
A BiPAP machine includes a motor, humidifier, tubing, and mask․ These components work together to deliver pressurized air, ensuring effective ventilation and patient comfort during therapy․
Key Components of a BiPAP Device
A BiPAP device comprises essential components that ensure optimal functionality․ The motor generates airflow, while the humidifier adds moisture to prevent dryness․ Tubing connects the motor to the mask, delivering pressurized air․ The mask or interface is crucial for comfort and proper fit․ Additional features like filters and sensors enhance performance and safety․ These components work synergistically to deliver precise IPAP and EPAP pressures, tailored to individual patient needs․ Proper maintenance and assembly of these parts are vital for effective therapy and patient comfort․
IPAP and EPAP Settings Explained
IPAP (Inspiratory Positive Airway Pressure) and EPAP (Expiratory Positive Airway Pressure) are core settings in BiPAP therapy․ IPAP delivers higher pressure during inhalation to assist breathing, while EPAP maintains a lower pressure during exhalation to keep airways open․ These pressures are adjusted based on patient needs, ensuring effective ventilation․ Proper titration of IPAP and EPAP balances comfort and therapeutic efficacy, preventing apneas and hypopneas․ Clinicians often start with baseline settings and fine-tune them during sleep studies or titration protocols, optimizing airflow and patient comfort for successful therapy outcomes․
BiPAP Settings for Sleep Apnea
BiPAP is commonly used to treat sleep apnea, delivering tailored pressures to maintain airway patency․ Typical settings include IPAP (10-20 cm H2O) and EPAP (5-15 cm H2O), adjusted per patient needs․
Common BiPAP Settings for Sleep Apnea
Common BiPAP settings for sleep apnea typically include an inspiratory positive airway pressure (IPAP) range of 10-20 cm H2O and an expiratory positive airway pressure (EPAP) range of 5-15 cm H2O․ These settings are adjusted based on the severity of sleep apnea and individual patient needs․ A starting point often includes IPAP at 12-15 cm H2O and EPAP at 8-10 cm H2O․ The difference between IPAP and EPAP, known as the pressure support, is usually set between 4-8 cm H2O to ensure comfortable breathing․ These settings are tailored during titration studies to optimize therapy effectiveness and patient comfort, addressing both obstructive and central sleep apnea events effectively․
Adjusting IPAP and EPAP for Optimal Therapy
Adjusting IPAP and EPAP settings is critical for optimal BiPAP therapy․ IPAP (inspiratory positive airway pressure) and EPAP (expiratory positive airway pressure) are tailored to address individual patient needs․ The process begins with baseline settings, which are then fine-tuned during titration studies to ensure effective airway pressure support․ IPAP is typically adjusted to eliminate respiratory events, while EPAP is set to maintain airway patency during exhalation․ Pressure support, the difference between IPAP and EPAP, is often set between 4-8 cm H2O to enhance comfort and breathing efficiency․ Continuous monitoring of tidal volumes, leak rates, and patient response guides further adjustments, ensuring therapy remains effective and comfortable over time․

Clinical Applications of BiPAP
BIPAP is widely used in non-invasive ventilation, supporting patients with respiratory failure, sleep apnea, and chronic respiratory conditions․ It provides targeted pressure support for improved breathing outcomes․
BiPAP in Non-Invasive Ventilation
BIPAP is a cornerstone in non-invasive ventilation, providing dual-level pressure support to assist patients with respiratory failure․ It delivers higher pressure during inhalation (IPAP) and lower during exhalation (EPAP), improving breathing patterns․ This therapy is widely used for conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), acute respiratory failure, and neuromuscular disorders․ Non-invasive ventilation with BIPAP reduces the need for intubation, enhances patient comfort, and promotes earlier recovery․ Proper adjustment of IPAP and EPAP settings is critical to ensure effective ventilation and prevent complications․ Clinical guidelines recommend titrating pressures based on patient response and tidal volumes, ensuring optimal therapy outcomes․
Using BiPAP in Acute Respiratory Care
BiPAP is a critical tool in acute respiratory care for patients with breathing difficulties․ It provides dual-level air pressure support, with higher pressure during inhalation (IPAP) and lower during exhalation (EPAP)․ This therapy is particularly effective in treating acute respiratory failure, COPD exacerbations, and other conditions requiring immediate ventilatory support․ BiPAP’s non-invasive nature reduces the need for intubation, lowering risks and improving patient comfort․ In emergency settings, healthcare providers must closely monitor patients, adjusting BiPAP settings based on clinical response and guidelines to ensure optimal outcomes․ Proper mask fitting is essential to prevent leaks and maintain effective pressure delivery, enhancing both therapy efficacy and patient tolerance․

Initial Setup and Titration
Initial BiPAP setup involves configuring IPAP and EPAP based on prescribed settings․ Titration is done to optimize therapy, ensuring proper pressure delivery and patient comfort, guided by clinical protocols․
Guidelines for Setting Up BiPAP
Setting up BiPAP involves configuring IPAP and EPAP based on prescribed settings, ensuring proper mask fit, and adjusting oxygen levels as needed․ Use a heated humidifier for comfort and start with low FiO2, titrating to achieve desired saturation․ Perform a Learn Circuit to detect leaks and optimize therapy․ Monitor tidal volumes and respiratory rate to ensure effective ventilation․ Adjust IPAP to control inspiratory pressure and EPAP for expiratory support․ Regularly review and titrate settings based on patient response and clinical guidelines to ensure optimal therapy outcomes and patient comfort․ Always refer to the device’s user manual for specific setup instructions․
Titration Protocol for BiPAP Settings
A titration protocol for BiPAP settings involves gradual adjustments to IPAP and EPAP to optimize therapy․ Start with prescribed settings and monitor patient responses, adjusting pressures to eliminate apneas and hypopneas․ Increase IPAP if inspiratory flow limitation is observed and adjust EPAP to maintain upper airway patency․ Tidal volumes and respiratory rate should be monitored to ensure effective ventilation․ Oxygen levels may be titrated to achieve target saturation, typically above 90%․ Regular clinical assessments and patient feedback guide further adjustments․ The process aims to balance therapeutic efficacy with patient comfort, ensuring minimal side effects like mask leaks or pressure discomfort․ Titration should be documented and reviewed by healthcare providers to confirm optimal settings․

Monitoring and Adjustments
Continuous monitoring of tidal volumes, leak rates, and patient response is essential․ Adjustments to IPAP, EPAP, and oxygen levels may be needed to optimize therapy and comfort․
Monitoring Tidal Volumes and Leak Rates

Tidal volumes and leak rates are critical metrics in BiPAP therapy․ Monitoring these ensures effective ventilation and prevents complications․ Tidal volumes should align with patient-specific targets, typically between 400-600 mL for adults, reflecting normal breathing patterns․ Leak rates, measured by the machine, must stay below 30 L/min to maintain pressure integrity․ Excessive leaks can reduce therapy efficacy and cause discomfort, necessitating mask adjustments or resizing․ Regular checks and adjustments by healthcare providers optimize therapy outcomes, ensuring patient comfort and therapeutic success․ Proper monitoring ensures BiPAP functions correctly, addressing respiratory needs effectively․
Adjusting Oxygen Levels in BiPAP Therapy
Oxygen levels in BiPAP therapy are tailored to meet individual patient needs․ Clinicians typically start with FiO2 at 100% and titrate down based on patient response․ Maintaining appropriate oxygenation is crucial for preventing hypoxemia․ Continuous monitoring of oxygen saturation via pulse oximetry guides adjustments․ Settings may vary depending on the severity of respiratory distress and underlying conditions․ Ensuring optimal oxygen levels enhances the effectiveness of BiPAP, promoting patient comfort and clinical stability․ Regular assessments and adjustments by healthcare providers are essential to maintain therapeutic efficacy and avoid complications․

Advanced Features of BiPAP
Advanced BiPAP features include AVAPS for consistent tidal volumes, heated humidifiers for enhanced comfort, and adaptive algorithms to optimize breathing patterns․ These features improve therapy efficacy and patient comfort․
AVAPS (Average Volume-Assured Pressure Support)
AVAPS, or Average Volume-Assured Pressure Support, is an advanced feature in BiPAP therapy designed to maintain a consistent tidal volume․ This technology automatically adjusts the inspiratory pressure to ensure that the patient receives the prescribed average tidal volume, typically set between 7-9 mL/kg․ By continuously monitoring the patient’s breathing, AVAPS compensates for changes in lung function or resistance, providing a more stable and effective therapy․ This feature is particularly beneficial for patients with varying respiratory needs, as it ensures that their ventilation remains consistent and comfortable․ AVAPS is often recommended for patients who require precise control over their tidal volumes to enhance respiratory support and improve clinical outcomes․ This adaptive technology helps in reducing the work of breathing and promotes better sleep quality, making it a valuable addition to BiPAP therapy․
Heated Humidifier Settings for Comfort
The heated humidifier in BiPAP therapy enhances comfort by adding moisture to the delivered air, reducing nasal congestion and throat irritation․ Proper settings involve adjusting the temperature between 1-6 levels, depending on the device, to prevent rainout and ensure optimal humidity․ It’s crucial to avoid over-humidification, which can cause condensation in the tubing․ Patients should adjust the humidifier based on their comfort level, typically starting at a lower setting and increasing as needed․ Regular cleaning and using distilled water are recommended to maintain hygiene and functionality․ Properly configured heated humidifier settings can significantly improve therapy tolerance and adherence, making BiPAP more effective for long-term use․

Troubleshooting Common Issues
Common BiPAP issues include mask leaks, pressure discomfort, and alarm triggers․ Regularly inspect masks for proper fit and adjust IPAP/EPAP settings to prevent discomfort․ Consult the user manual for guidance on resolving these issues effectively․
Resolving Mask Leaks and Pressure Issues
Mask leaks and pressure issues are common challenges in BiPAP therapy․ To resolve leaks, ensure the mask fits snugly and adjust the headgear as needed․ Regularly inspect the mask for signs of wear or damage․ If leaks persist, consider trying a different mask size or type․ Pressure issues can often be addressed by fine-tuning the IPAP and EPAP settings․ Lowering the pressure may reduce discomfort, while increasing it might improve breathing․ Always refer to the user manual or consult a healthcare professional for guidance․ Proper troubleshooting ensures effective therapy and enhances patient comfort․
Troubleshooting Alarm Settings on BiPAP
BiPAP alarms are designed to alert users of potential issues, such as low oxygen levels, high leak rates, or device malfunctions․ To address these, first, check the tubing and mask for any blockages or leaks․ Ensure the mask fits properly and adjust the headgear if necessary․ If the alarm persists, review the prescribed settings and compare them with the machine’s current configuration․ Adjusting the IPAP or EPAP levels may resolve pressure-related alarms․ For oxygen-related alerts, verify the oxygen supply and ensure it is within the prescribed range․ Refer to the user manual or consult a healthcare professional for complex issues․ Regular maintenance and proper setup can help minimize alarm triggers and ensure smooth therapy․
Proper BiPAP settings are vital for effective therapy, ensuring comfort and efficacy․ Adherence to clinical guidelines and patient-specific adjustments maximize benefits․ Future advancements promise enhanced customization and improved outcomes․
Best practices for BiPAP settings emphasize proper initialization and titration to ensure efficacy and comfort․ Start with prescribed IPAP and EPAP levels, adjusting based on patient response and sleep study data․ Regular monitoring of tidal volumes, leak rates, and oxygen levels is essential for optimal therapy․ Utilize AVAPS for consistent tidal volumes and heated humidifiers for comfort․ Ensure proper mask fit and perform routine device checks․ Patient-specific adjustments, guided by clinical expertise, are critical for addressing individual needs․ Adherence to these practices ensures effective therapy, improves adherence, and enhances overall patient outcomes in both sleep apnea and respiratory care settings․
Future Directions in BiPAP Technology
Future advancements in BiPAP technology aim to enhance patient comfort, improve efficacy, and integrate advanced monitoring systems․ Innovations like automated pressure adjustment and AI-driven algorithms are expected to optimize therapy delivery․ Portable and wearable BiPAP devices are being developed for greater convenience․ Integration with telemedicine platforms could enable remote monitoring and adjustments, improving access to care․ Research into personalized therapy settings, tailored to individual physiological needs, is ongoing․ Additionally, advancements in noise reduction and mask design are anticipated to improve adherence․ These developments will likely make BiPAP therapy more accessible, effective, and patient-centric, addressing a broader range of respiratory conditions and enhancing overall outcomes․

